Nudged Elastic Band¶
In this tutorial, we will determine the activation energies of Li diffusion along the [010] and [001] directions (referred to as paths b and c respectively) in lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO_4), a cathode material for lithium ion batteries.
DFT references energies are:
Barrier heights:
path b = 0.27 eV
path c = 2.5 eV
(see table 1 in https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA05062F)
Set up environment (optional)¶
These steps are required to run this tutorial with Google Colab. To do so, uncomment and run the cell below.
This will replace pre-installed versions of numpy and torch in Colab with versions that are known to be compatible with janus-core.
It may be possible to skip the steps that uninstall and reinstall torch, which will save a considerable amount of time.
These instructions but may work for other systems too, but it is typically preferable to prepare a virtual environment separately before running this notebook if possible.
[1]:
# import locale
# locale.getpreferredencoding = lambda: "UTF-8"
# ! pip uninstall numpy -y # Uninstall pre-installed numpy
# ! pip uninstall torch torchaudio torchvision transformers -y # Uninstall pre-installed torch
# ! uv pip install torch==2.5.1 # Install pinned version of torch
# ! uv pip install janus-core[mace,orb,chgnet,visualise] data-tutorials --system # Install janus-core with MACE, Orb, CHGNet, and WeasWidget, and data-tutorials
# get_ipython().kernel.do_shutdown(restart=True) # Restart kernel to update libraries. This may warn that your session has crashed.
To ensure you have the latest version of janus-core installed, compare the output of the following cell to the latest version available at https://pypi.org/project/janus-core/
[2]:
from janus_core import __version__
print(__version__)
0.8.7
Prepare data, modules, and model parameters¶
You can toggle the following to investigate different models:
[3]:
model_params = {"arch": "mace_mp", "model": "medium-0b3"}
# model_params = {"arch": "mace_mp", "model": "medium-mpa-0"}
# model_params = {"arch": "mace_mp", "model": "medium-omat-0"}
# model_params = {"arch": "chgnet"}
# model_params = {"arch": "orb"}
[4]:
from weas_widget import WeasWidget
from ase.io import read
from data_tutorials.data import get_data
from janus_core.calculations.geom_opt import GeomOpt
from janus_core.calculations.neb import NEB
Use data_tutorials to get the data required for this tutorial:
[5]:
get_data(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stfc/janus-core/main/docs/source/tutorials/data/",
filename="LiFePO4_supercell.cif",
folder="data",
)
try to download LiFePO4_supercell.cif from https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stfc/janus-core/main/docs/source/tutorials/data/ and save it in data/LiFePO4_supercell.cif
saved in data/LiFePO4_supercell.cif
Preparing end structures¶
The initial structure can be downloaded from the Materials Project (mp-19017):
[6]:
LFPO = read("data/LiFePO4_supercell.cif")
v=WeasWidget()
v.from_ase(LFPO)
v.avr.model_style = 1
v.avr.show_hydrogen_bonds = True
v
[6]:
First, we will relax the supercell:
[7]:
GeomOpt(struct=LFPO, **model_params).run()
v1=WeasWidget()
v1.from_ase(LFPO)
v1.avr.model_style = 1
v1.avr.show_hydrogen_bonds = True
v1
/home/runner/work/janus-core/janus-core/.venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/e3nn/o3/_wigner.py:10: UserWarning: Environment variable TORCH_FORCE_NO_WEIGHTS_ONLY_LOAD detected, since the`weights_only` argument was not explicitly passed to `torch.load`, forcing weights_only=False.
_Jd, _W3j_flat, _W3j_indices = torch.load(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'constants.pt'))
cuequivariance or cuequivariance_torch is not available. Cuequivariance acceleration will be disabled.
Downloading MACE model from 'https://github.com/ACEsuit/mace-mp/releases/download/mace_mp_0b3/mace-mp-0b3-medium.model'
Cached MACE model to /home/runner/.cache/mace/macemp0b3mediummodel
Using Materials Project MACE for MACECalculator with /home/runner/.cache/mace/macemp0b3mediummodel
Using float64 for MACECalculator, which is slower but more accurate. Recommended for geometry optimization.
Using head default out of ['default']
/home/runner/work/janus-core/janus-core/.venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/mace/calculators/mace.py:197: UserWarning: Environment variable TORCH_FORCE_NO_WEIGHTS_ONLY_LOAD detected, since the`weights_only` argument was not explicitly passed to `torch.load`, forcing weights_only=False.
torch.load(f=model_path, map_location=device)
Step Time Energy fmax
LBFGS: 0 13:41:37 -762.842666 0.654854
LBFGS: 1 13:41:39 -763.038742 0.437508
LBFGS: 2 13:41:41 -763.090096 0.392867
LBFGS: 3 13:41:43 -763.119488 0.374220
LBFGS: 4 13:41:45 -763.172830 0.346620
LBFGS: 5 13:41:46 -763.213488 0.334927
LBFGS: 6 13:41:48 -763.256842 0.327520
LBFGS: 7 13:41:50 -763.297792 0.328964
LBFGS: 8 13:41:52 -763.342419 0.332009
LBFGS: 9 13:41:54 -763.385108 0.328513
LBFGS: 10 13:41:56 -763.427187 0.308144
LBFGS: 11 13:41:58 -763.474267 0.274918
LBFGS: 12 13:41:59 -763.528185 0.234548
LBFGS: 13 13:42:01 -763.579927 0.246328
LBFGS: 14 13:42:03 -763.627605 0.245408
LBFGS: 15 13:42:05 -763.684752 0.231582
LBFGS: 16 13:42:06 -763.766360 0.283626
LBFGS: 17 13:42:08 -763.855346 0.296599
LBFGS: 18 13:42:10 -763.931149 0.188692
LBFGS: 19 13:42:12 -763.965778 0.154808
LBFGS: 20 13:42:14 -763.996599 0.213159
LBFGS: 21 13:42:15 -764.039520 0.255107
LBFGS: 22 13:42:17 -764.108589 0.255570
LBFGS: 23 13:42:19 -764.175608 0.200210
LBFGS: 24 13:42:21 -764.208816 0.096659
[7]:
Next, we will create the start and end structures:
[8]:
# NEB path along b and c directions have the same starting image.
# For start bc remove site 5
LFPO_start_bc = LFPO.copy()
del LFPO_start_bc[5]
# For end b remove site 11
LFPO_end_b = LFPO.copy()
del LFPO_end_b[11]
# For end c remove site 4
LFPO_end_c = LFPO.copy()
del LFPO_end_c[4]
Path b¶
We can now calculate the barrier height along path b.
This also includes running geometry optimization on the end points of this path.
[9]:
n_images = 7
interpolator="pymatgen" # ASE interpolation performs poorly in this case
neb_b = NEB(
init_struct=LFPO_start_bc,
final_struct=LFPO_end_b,
n_images=n_images,
interpolator=interpolator,
minimize=True,
fmax=0.1,
**model_params,
)
Using Materials Project MACE for MACECalculator with /home/runner/.cache/mace/macemp0b3mediummodel
Using float64 for MACECalculator, which is slower but more accurate. Recommended for geometry optimization.
Using head default out of ['default']
/home/runner/work/janus-core/janus-core/.venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/mace/calculators/mace.py:197: UserWarning: Environment variable TORCH_FORCE_NO_WEIGHTS_ONLY_LOAD detected, since the`weights_only` argument was not explicitly passed to `torch.load`, forcing weights_only=False.
torch.load(f=model_path, map_location=device)
[10]:
results = neb_b.run()
Step Time Energy fmax
LBFGS: 0 13:42:23 -758.975432 1.930990
LBFGS: 1 13:42:24 -759.140669 0.711957
LBFGS: 2 13:42:26 -759.209571 0.514600
LBFGS: 3 13:42:28 -759.298948 0.404890
LBFGS: 4 13:42:29 -759.316304 0.265548
LBFGS: 5 13:42:31 -759.336518 0.252446
LBFGS: 6 13:42:33 -759.351338 0.330410
LBFGS: 7 13:42:35 -759.368546 0.309163
LBFGS: 8 13:42:36 -759.378014 0.229741
LBFGS: 9 13:42:38 -759.386280 0.221552
LBFGS: 10 13:42:40 -759.395290 0.278156
LBFGS: 11 13:42:41 -759.404981 0.291370
LBFGS: 12 13:42:43 -759.411852 0.192426
LBFGS: 13 13:42:45 -759.415355 0.075502
Step Time Energy fmax
LBFGS: 0 13:42:47 -758.975436 1.930961
LBFGS: 1 13:42:48 -759.140671 0.711930
LBFGS: 2 13:42:50 -759.209572 0.514582
LBFGS: 3 13:42:52 -759.298949 0.404887
LBFGS: 4 13:42:53 -759.316305 0.265544
LBFGS: 5 13:42:55 -759.336519 0.252446
LBFGS: 6 13:42:57 -759.351338 0.330395
LBFGS: 7 13:42:59 -759.368546 0.309158
LBFGS: 8 13:43:00 -759.378015 0.229745
LBFGS: 9 13:43:02 -759.386281 0.221556
LBFGS: 10 13:43:04 -759.395291 0.278147
LBFGS: 11 13:43:05 -759.404982 0.291359
LBFGS: 12 13:43:07 -759.411852 0.192423
LBFGS: 13 13:43:09 -759.415355 0.075502
Step Time fmax
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 0 13:43:44 1.5090
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 1 13:43:56 1.1032
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 2 13:44:08 0.9983
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 3 13:44:20 0.8704
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 4 13:44:31 0.8013
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 5 13:44:43 0.7712
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 6 13:44:55 0.7441
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 7 13:45:07 0.6738
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 8 13:45:19 0.4346
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 9 13:45:43 0.4299
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 10 13:45:55 0.4226
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 11 13:46:07 0.3946
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 12 13:46:19 0.2843
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 13 13:46:43 0.2726
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 14 13:46:55 0.2652
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 15 13:47:06 0.2612
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 16 13:47:18 0.2552
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 17 13:47:30 0.2323
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 18 13:47:54 0.2219
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 19 13:48:06 0.2141
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 20 13:48:18 0.2087
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 21 13:48:30 0.2055
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 22 13:48:42 0.2005
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 23 13:48:54 0.1809
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 24 13:49:18 0.1729
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 25 13:49:30 0.1664
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 26 13:49:42 0.1624
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 27 13:49:55 0.1598
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 28 13:50:07 0.1559
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 29 13:50:19 0.1409
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 30 13:50:31 0.2612
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 31 13:50:55 0.0826
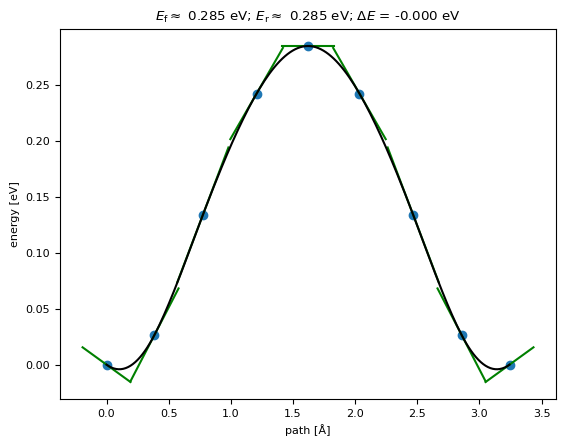
The results include the barrier (without any interpolation between highest images) and maximum force at the point in the simulation
[11]:
print(results)
{'barrier': np.float64(0.2847173696816294), 'delta_E': np.float64(-1.6499575394846033e-07), 'max_force': np.float64(0.09009922957482004)}
We can also plot the band:
[12]:
fig = neb_b.nebtools.plot_band()
v1=WeasWidget()
v1.from_ase(neb_b.nebtools.images)
v1.avr.model_style = 1
v1.avr.show_hydrogen_bonds = True
v1
[12]:
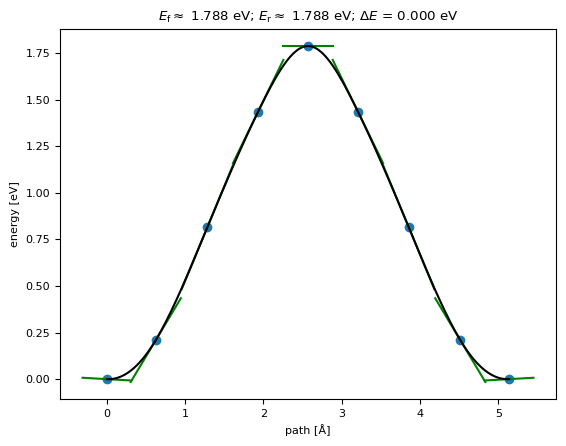
Path c¶
We can calculate the barrier height along path c similarly
[13]:
n_images = 7
interpolator="pymatgen"
neb_c = NEB(
init_struct=LFPO_start_bc,
final_struct=LFPO_end_c,
n_images=n_images,
interpolator=interpolator,
minimize=True,
fmax=0.1,
**model_params,
)
Using Materials Project MACE for MACECalculator with /home/runner/.cache/mace/macemp0b3mediummodel
Using float64 for MACECalculator, which is slower but more accurate. Recommended for geometry optimization.
Using head default out of ['default']
/home/runner/work/janus-core/janus-core/.venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/mace/calculators/mace.py:197: UserWarning: Environment variable TORCH_FORCE_NO_WEIGHTS_ONLY_LOAD detected, since the`weights_only` argument was not explicitly passed to `torch.load`, forcing weights_only=False.
torch.load(f=model_path, map_location=device)
[14]:
results = neb_c.run()
Step Time Energy fmax
LBFGS: 0 13:51:00 -759.415355 0.075502
Step Time Energy fmax
LBFGS: 0 13:51:02 -758.975431 1.930990
LBFGS: 1 13:51:04 -759.140669 0.711958
LBFGS: 2 13:51:06 -759.209571 0.514601
LBFGS: 3 13:51:08 -759.298948 0.404890
LBFGS: 4 13:51:09 -759.316304 0.265548
LBFGS: 5 13:51:11 -759.336518 0.252446
LBFGS: 6 13:51:13 -759.351338 0.330410
LBFGS: 7 13:51:14 -759.368546 0.309163
LBFGS: 8 13:51:16 -759.378014 0.229741
LBFGS: 9 13:51:18 -759.386280 0.221553
LBFGS: 10 13:51:20 -759.395290 0.278156
LBFGS: 11 13:51:21 -759.404981 0.291370
LBFGS: 12 13:51:23 -759.411852 0.192426
LBFGS: 13 13:51:25 -759.415355 0.075502
Step Time fmax
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 0 13:52:01 2.3204
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 1 13:52:13 1.6499
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 2 13:52:25 0.9977
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 3 13:52:38 0.6537
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 4 13:53:02 0.4186
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 5 13:53:14 0.3969
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 6 13:53:26 0.3176
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 7 13:53:50 0.2998
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 8 13:54:15 0.2690
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 9 13:54:27 0.2608
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 10 13:54:39 0.2293
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 11 13:55:04 0.2186
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 12 13:55:17 0.2622
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 13 13:55:29 0.2009
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 14 13:55:41 0.1946
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 15 13:55:53 0.1883
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 16 13:56:06 0.1653
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 17 13:56:30 0.1600
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 18 13:56:42 0.1538
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 19 13:56:55 0.1475
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 20 13:57:07 0.1379
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 21 13:57:19 0.1346
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 22 13:57:31 0.1288
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 23 13:57:44 0.1263
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 24 13:57:56 0.1169
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 25 13:58:08 0.1806
NEBOptimizer[ode]: 26 13:58:33 0.0821
[15]:
print(results)
{'barrier': np.float64(1.787575440772347), 'delta_E': np.float64(4.249386620358564e-09), 'max_force': np.float64(0.09762768267248513)}
[16]:
fig = neb_c.nebtools.plot_band()
v2=WeasWidget()
v2.from_ase(neb_c.nebtools.images)
v2.avr.model_style = 1
v2.avr.show_hydrogen_bonds = True
v2
[16]: